Design Thinking: Unleashing Creativity and Innovation
Design Thinking: Unleashing Creativity and Innovation
Design Thinking: Unleashing Creativity and Innovation
Design Thinking: Unleashing Creativity and Innovation
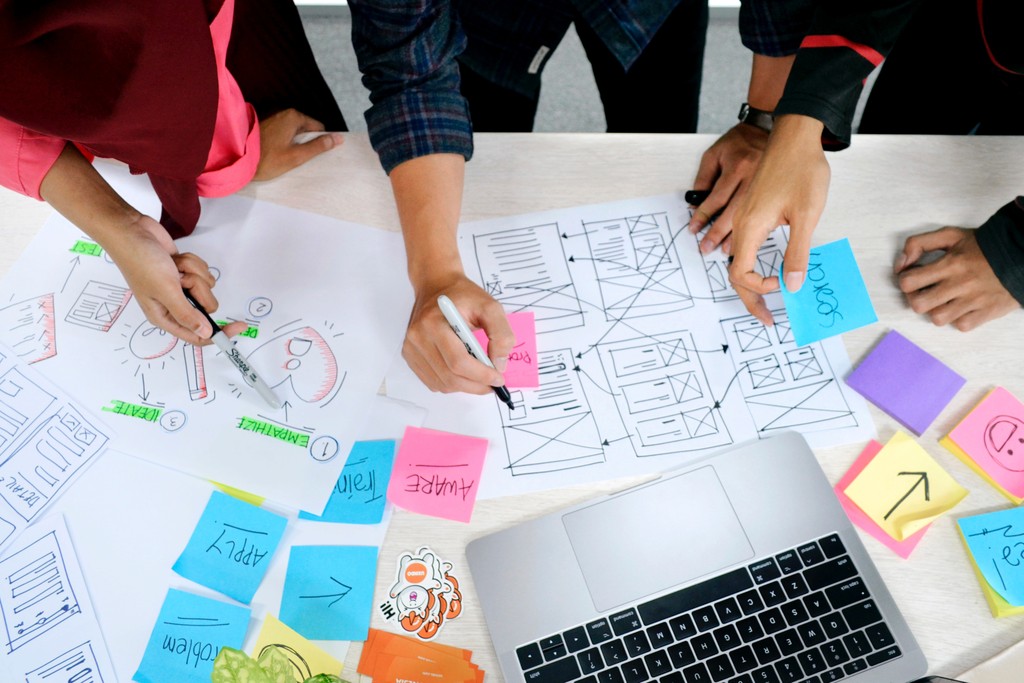




Understanding Design Thinking
At its core, design thinking revolves around understanding and empathizing with the needs and desires of end-users. Instead of assuming what customers want, designers immerse themselves in the users' experiences through interviews, observations, and other research methods. This empathetic understanding forms the foundation for all subsequent stages of the process.
The Five Stages of Design Thinking
Empathize: The first stage involves gaining a deep understanding of the users and their needs. Designers interact with the target audience to gather insights, identify pain points, and define the problem from the users' perspective.
Define: In this stage, designers synthesize the data collected during the empathize phase to define the core problem and create a clear problem statement. This step ensures that the team focuses on solving the right problem for the right audience.
Ideate: During the ideation phase, creative thinking takes center stage. Brainstorming sessions and other creative techniques are employed to generate a wide range of possible solutions without any judgment. The goal is to foster a collaborative environment where all ideas are welcomed.
Prototype: Prototyping involves transforming selected ideas from the ideation phase into tangible representations. These can be rough sketches, digital mock-ups, or even physical models. Prototypes help designers test their assumptions and gather valuable feedback from users before committing to a full-scale solution.
Test: The final stage revolves around testing the prototypes with real users. This iterative process allows designers to refine their ideas based on feedback and further optimize the solution. By continuously refining the design through testing, the final product or service becomes more likely to meet the users' needs effectively.
Key Principles of Design Thinking
Human-Centered Approach: Understanding and addressing the needs, motivations, and emotions of users is fundamental to design thinking. By prioritizing human experiences, designers create solutions that resonate with their target audience.
Collaboration and Diversity: Design thinking emphasizes cross-functional teamwork and diverse perspectives. Collaborative efforts from individuals with different backgrounds, expertise, and experiences can lead to more innovative and holistic solutions.
Iterative Process: Design thinking is not a linear path; it is iterative and flexible. Designers continuously learn from testing and feedback, refining their ideas and iterating on the solution until they achieve the desired outcome.
Embracing Ambiguity and Failure: Design thinking encourages embracing uncertainty and learning from failures. Designers are encouraged to take risks, learn from mistakes, and iterate based on insights gained from experimentation.
The Impact of Design Thinking
Design thinking has demonstrated its potential to foster creativity and innovation in various sectors. Companies like Apple, Airbnb, and Google have successfully embraced design thinking principles to create groundbreaking products and services that have reshaped entire industries.
Beyond business, design thinking has proven valuable in addressing complex social challenges. From healthcare to education and environmental issues, design thinking has helped in developing sustainable and impactful solutions by considering the needs of all stakeholders involved.
date published
Jan 27, 2022
reading time
8 min
Understanding Design Thinking
At its core, design thinking revolves around understanding and empathizing with the needs and desires of end-users. Instead of assuming what customers want, designers immerse themselves in the users' experiences through interviews, observations, and other research methods. This empathetic understanding forms the foundation for all subsequent stages of the process.
The Five Stages of Design Thinking
Empathize: The first stage involves gaining a deep understanding of the users and their needs. Designers interact with the target audience to gather insights, identify pain points, and define the problem from the users' perspective.
Define: In this stage, designers synthesize the data collected during the empathize phase to define the core problem and create a clear problem statement. This step ensures that the team focuses on solving the right problem for the right audience.
Ideate: During the ideation phase, creative thinking takes center stage. Brainstorming sessions and other creative techniques are employed to generate a wide range of possible solutions without any judgment. The goal is to foster a collaborative environment where all ideas are welcomed.
Prototype: Prototyping involves transforming selected ideas from the ideation phase into tangible representations. These can be rough sketches, digital mock-ups, or even physical models. Prototypes help designers test their assumptions and gather valuable feedback from users before committing to a full-scale solution.
Test: The final stage revolves around testing the prototypes with real users. This iterative process allows designers to refine their ideas based on feedback and further optimize the solution. By continuously refining the design through testing, the final product or service becomes more likely to meet the users' needs effectively.
Key Principles of Design Thinking
Human-Centered Approach: Understanding and addressing the needs, motivations, and emotions of users is fundamental to design thinking. By prioritizing human experiences, designers create solutions that resonate with their target audience.
Collaboration and Diversity: Design thinking emphasizes cross-functional teamwork and diverse perspectives. Collaborative efforts from individuals with different backgrounds, expertise, and experiences can lead to more innovative and holistic solutions.
Iterative Process: Design thinking is not a linear path; it is iterative and flexible. Designers continuously learn from testing and feedback, refining their ideas and iterating on the solution until they achieve the desired outcome.
Embracing Ambiguity and Failure: Design thinking encourages embracing uncertainty and learning from failures. Designers are encouraged to take risks, learn from mistakes, and iterate based on insights gained from experimentation.
The Impact of Design Thinking
Design thinking has demonstrated its potential to foster creativity and innovation in various sectors. Companies like Apple, Airbnb, and Google have successfully embraced design thinking principles to create groundbreaking products and services that have reshaped entire industries.
Beyond business, design thinking has proven valuable in addressing complex social challenges. From healthcare to education and environmental issues, design thinking has helped in developing sustainable and impactful solutions by considering the needs of all stakeholders involved.
date published
Jan 27, 2022
reading time
8 min
Understanding Design Thinking
At its core, design thinking revolves around understanding and empathizing with the needs and desires of end-users. Instead of assuming what customers want, designers immerse themselves in the users' experiences through interviews, observations, and other research methods. This empathetic understanding forms the foundation for all subsequent stages of the process.
The Five Stages of Design Thinking
Empathize: The first stage involves gaining a deep understanding of the users and their needs. Designers interact with the target audience to gather insights, identify pain points, and define the problem from the users' perspective.
Define: In this stage, designers synthesize the data collected during the empathize phase to define the core problem and create a clear problem statement. This step ensures that the team focuses on solving the right problem for the right audience.
Ideate: During the ideation phase, creative thinking takes center stage. Brainstorming sessions and other creative techniques are employed to generate a wide range of possible solutions without any judgment. The goal is to foster a collaborative environment where all ideas are welcomed.
Prototype: Prototyping involves transforming selected ideas from the ideation phase into tangible representations. These can be rough sketches, digital mock-ups, or even physical models. Prototypes help designers test their assumptions and gather valuable feedback from users before committing to a full-scale solution.
Test: The final stage revolves around testing the prototypes with real users. This iterative process allows designers to refine their ideas based on feedback and further optimize the solution. By continuously refining the design through testing, the final product or service becomes more likely to meet the users' needs effectively.
Key Principles of Design Thinking
Human-Centered Approach: Understanding and addressing the needs, motivations, and emotions of users is fundamental to design thinking. By prioritizing human experiences, designers create solutions that resonate with their target audience.
Collaboration and Diversity: Design thinking emphasizes cross-functional teamwork and diverse perspectives. Collaborative efforts from individuals with different backgrounds, expertise, and experiences can lead to more innovative and holistic solutions.
Iterative Process: Design thinking is not a linear path; it is iterative and flexible. Designers continuously learn from testing and feedback, refining their ideas and iterating on the solution until they achieve the desired outcome.
Embracing Ambiguity and Failure: Design thinking encourages embracing uncertainty and learning from failures. Designers are encouraged to take risks, learn from mistakes, and iterate based on insights gained from experimentation.
The Impact of Design Thinking
Design thinking has demonstrated its potential to foster creativity and innovation in various sectors. Companies like Apple, Airbnb, and Google have successfully embraced design thinking principles to create groundbreaking products and services that have reshaped entire industries.
Beyond business, design thinking has proven valuable in addressing complex social challenges. From healthcare to education and environmental issues, design thinking has helped in developing sustainable and impactful solutions by considering the needs of all stakeholders involved.
date published
Jan 27, 2022
reading time
8 min
Understanding Design Thinking
At its core, design thinking revolves around understanding and empathizing with the needs and desires of end-users. Instead of assuming what customers want, designers immerse themselves in the users' experiences through interviews, observations, and other research methods. This empathetic understanding forms the foundation for all subsequent stages of the process.
The Five Stages of Design Thinking
Empathize: The first stage involves gaining a deep understanding of the users and their needs. Designers interact with the target audience to gather insights, identify pain points, and define the problem from the users' perspective.
Define: In this stage, designers synthesize the data collected during the empathize phase to define the core problem and create a clear problem statement. This step ensures that the team focuses on solving the right problem for the right audience.
Ideate: During the ideation phase, creative thinking takes center stage. Brainstorming sessions and other creative techniques are employed to generate a wide range of possible solutions without any judgment. The goal is to foster a collaborative environment where all ideas are welcomed.
Prototype: Prototyping involves transforming selected ideas from the ideation phase into tangible representations. These can be rough sketches, digital mock-ups, or even physical models. Prototypes help designers test their assumptions and gather valuable feedback from users before committing to a full-scale solution.
Test: The final stage revolves around testing the prototypes with real users. This iterative process allows designers to refine their ideas based on feedback and further optimize the solution. By continuously refining the design through testing, the final product or service becomes more likely to meet the users' needs effectively.
Key Principles of Design Thinking
Human-Centered Approach: Understanding and addressing the needs, motivations, and emotions of users is fundamental to design thinking. By prioritizing human experiences, designers create solutions that resonate with their target audience.
Collaboration and Diversity: Design thinking emphasizes cross-functional teamwork and diverse perspectives. Collaborative efforts from individuals with different backgrounds, expertise, and experiences can lead to more innovative and holistic solutions.
Iterative Process: Design thinking is not a linear path; it is iterative and flexible. Designers continuously learn from testing and feedback, refining their ideas and iterating on the solution until they achieve the desired outcome.
Embracing Ambiguity and Failure: Design thinking encourages embracing uncertainty and learning from failures. Designers are encouraged to take risks, learn from mistakes, and iterate based on insights gained from experimentation.
The Impact of Design Thinking
Design thinking has demonstrated its potential to foster creativity and innovation in various sectors. Companies like Apple, Airbnb, and Google have successfully embraced design thinking principles to create groundbreaking products and services that have reshaped entire industries.
Beyond business, design thinking has proven valuable in addressing complex social challenges. From healthcare to education and environmental issues, design thinking has helped in developing sustainable and impactful solutions by considering the needs of all stakeholders involved.
date published
Jan 27, 2022
reading time
8 min
.say hello
i'm open for freelance projects, feel free to email me to see how can we collaborate
.say hello
i'm open for freelance projects, feel free to email me to see how can we collaborate
.say hello
i'm open for freelance projects, feel free to email me to see how can we collaborate
.say hello